It’s safe to say the internet is a vast and diverse ecosystem, constantly growing and evolving. A lot of people are shocked to learn the true depth of the internet, which can be broken down into three sections: the surface or visible web, the deep web, and the dark web.
It’s complex, technical, and due to its ever-evolving nature, it can feel overwhelming and difficult to digest. But, like anything which intimidates or worries us, the first step to removing anxiety is to dive into learning and understanding how these things work. From there, we assess risk levels and consider small changes that can make a big difference.
First up, let’s explore the surface web
As of December 2023, there are currently around 1.1 billion websites in the world. In fact, right now there are about three new websites created every second. The catch, however, is these numbers represent websites residing on the surface web.
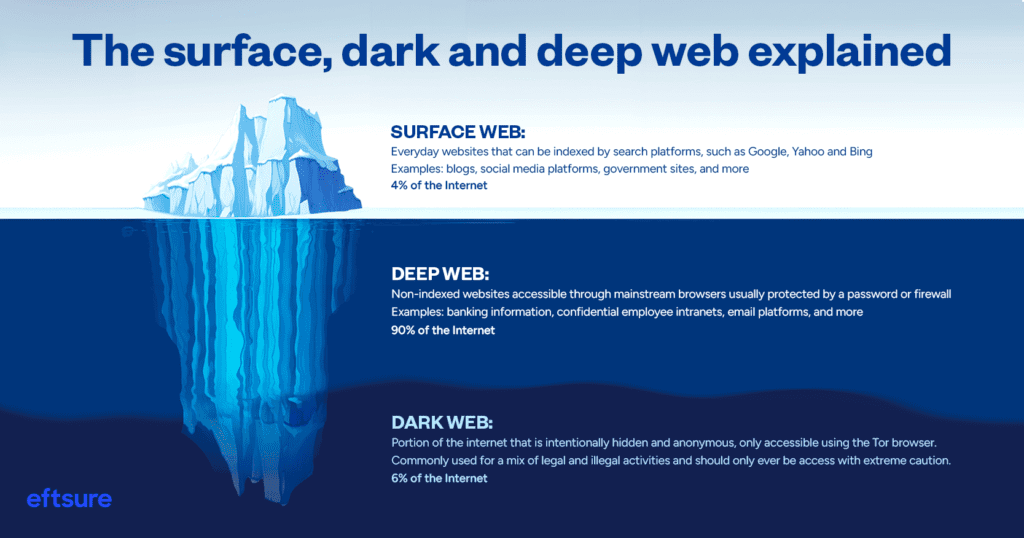
To put it simply, the surface web is the portion of the World Wide Web that can be indexed by search engines, such as Google, Yahoo, or Bing. These would be your everyday websites – for example, ecommerce sites, government websites, blogs, social media platforms, and more.
However large the surface web may seem, it only accounts for about 4% of the internet.
What is the deep web? Defined
When considering the surface web as the indexed portion of the World Wide Web, the deep web is simply the portion of the internet that cannot be indexed. The deep web is said to account for 90% of the internet, which really puts the size of the internet into perspective when we think about the number of websites accounting for the surface web.
Although you won’t find deep websites through a simple Google search, with the proper URL you can access these pages from your normal internet browser (i.e. Google Chrome, Safari, etc). An example of something on the deep web could be anything from a confidential employee-only intranet to cloud storage to the wedding website created to be shared with close friends and family. Generally, the only people who should land on these sites are those with a unique URL or access code.
What is the dark web? Defined with a brief history
Despite users of the dark web needing to be wary before jumping in, the number of people accessing the dark web is continuously snowballing. According to BDO, during Q3 of 2023, daily users of the dark web rose to 2.7 million, up by 200,000 from the same period in 2022.
Although constantly painted with a reputation for illicit and illegal activities, the dark web isn’t all bad news. In fact, the earliest usage of the dark web dates back to the late 1990s, where two research organizations in the US Department of Defense looked for new ways of secret and secure communication not traceable by foreign enemies.
Though it wasn’t necessarily intended for illicit purposes, there’s no denying its true potential wasn’t fully realized until much later.
Tor and accessing the dark web
Originally titled The Onion Routing Project, now called Tor Project for short, is an anonymous private network used to browse the dark web. As a continuation to the history behind the dark web, Tor was originally created and used by the US Navy before becoming free for anyone to use as an open-source network in 2002.
Leveraging the onion as an analogy, Tor has several layers and techniques for transmitting data. When users are browsing Tor, unlike the surface web where information is directed from the user directly to the site, using Tor the data is completely decentralized. Data will be routed and bounced through several different computers and relay points, making it completely and utterly impossible to trace.
Although the Tor software is a free download and it’s completely legal to use (it’s important to note the Tor web is not designed or intended for illegal activity), it’s important to know where you want Tor to take you – and what could be lurking when you get there. When it comes to the dark web, users should be prepared to confront a mix of the good, the bad, and the ugly.
Who uses the dark web?
Let’s start by recognizing the dark web has a diverse range of users with a diverse list of uses – not all of them nefarious.
Government agencies: as a nod to its original purpose, the dark web is still used today by government agencies for communication, to investigate criminal activity or to gather intelligence.
Whistleblowers and activists: people who want to report illegal or sensitive information with journalists or proper authorities – or those who are trying to evade oppressive governments – may turn to the dark web as a way to guarantee identity protection.
Journalists, privacy advocates, and researchers: in a professional capacity, these individuals may turn to the dark web to seek out opportunities to interview anonymous witnesses, sources of information or whistleblowers, seek out information on illegal markets and/or to publish their work.
Cryptocurrency investors: much of cryptocurrency was born out of the dark web audience, therefore it’s no surprise you’ll find many investors and advocates on the dark web for discussions, research, and trading in some capacity.
Criminals: and then, for every good group, you’ll often find a bad apple. And, unfortunately, the criminals of the dark web are what have given the space an extremely negative reputation. There’s a laundry list of uses for criminals on the dark web, including access to stolen data, selling drugs, hacking, and more. We detail this further, later in the article.
Legal use of the dark web and Tor Web
Despite its sinister reputation, Tor and the dark web infrastructure weren’t created with ill intentions. Here are a few of the top legal uses for the dark web which exist today:
Anonymous email services: email platforms such as ProtonMail (supported by the Tor network), among others, add an extra layer of anonymity over email accounts. These platforms guarantee lack of surveillance and heightened privacy than traditional email platforms on the surface web.
Circumvent government censorship: For those living under authoritarian governments with increased internet monitoring and heightened restrictions, a user can access the dark web to browse and search for information otherwise inaccessible to them.
Journalism and anonymity: in instances where people may not feel comfortable divulging their identity to journalists, dark web apps such as SecureDrop allow media to facilitate anonymous interviews with key sources. This is widely used by some of the biggest media outlets in the world today.
Access to news outlets: in addition to the above uses, many people live in places where they may not have access to trusted news sources, potentially blocked by their governments. The dark web allows people to find and read news otherwise censored or blocked on their local surface web. Key outlets such as the New York Times and BBC news have launched and maintained copies of their website on the dark web.
Access to academic research: The dark web is packed with scholarly and academic research. In fact, the American Journal of Freestanding Research Psychology hosts free academic papers on its dark web site – all legally accessible as the research has been approved by the original authors.
Cryptocurrency wallets: on the surface web, cryptocurrency transactions are all heavily traceable. On the dark web, there are options to add a veil of anonymity when it comes to exchanging coins or placing transactions.
Social media: with every web comes a craving for social media, and the dark web is not shy to hosting several different social media applications. Not only that, even platforms such as Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) are now hosting a version of their platforms on the dark web to allow users – ones who are banned from social channels due to government restrictions – access to the platforms without surveillance.
Illegal uses of the dark web
On the flip side, it’s no surprise there’s plenty of illegal activity happening on the dark web. And, unfortunately, it can be incredibly hard if not impossible to stop. These are some of the top illegal activities on the dark web, which are often highlighted in news and research today:
Hacking services and cybercrime: there are several opportunities to run into hacking tools on the dark web, including malware, even hacking-for-hire. Essentially users will look to gain unauthorized access to servers, steal data, and gain access to proprietary information.
Blackmail and extortion: alongside hacking services and cybercrime, criminals can use the dark web to demand ransom payments or threaten to publish sensitive, stolen information.
Stolen data and identity theft: also related to illegal hacking services, there are several communities on the dark web that will use stolen data, medical data, identity data, and more by selling it or committing identity theft.
Drug trade: the dark web is notorious for illegal drug sales, including prescription medication and other recreational drugs.
Money laundering: it is reported the dark web can be used by scammers to steal money and leverage services on the dark web to turn it into untraceable cash.
Hitmen services: lastly, other extremely unfortunate uses which have surfaced via the New York Times reports there have been instances where people have used the dark web in an attempt to hire a hitman service.
The true cost of criminal activity on the dark web
According to Privacy Affairs' Dark Web Price Index 2023, the dark web markets continue to grow as we head into the new year. To highlight a few from their list:
Credit card details, account balance up to $5000 | $110
Stolen online banking logins | $40
Switzerland online banking login | $2200
N26 verified crypto account | $2650
Hacked Facebook account | $25
Netflix account, 1-year subscriptions | $20
USA selfie holding ID | $110
Maltese passport | $4000
10 million USA email addresses | $120
The list is quite lengthy, but this gives a pretty good idea of how much can be purchased from the Dark Web.
Are dark web criminals ever prosecuted?
Once again referencing Privacy Affairs, during the later part of 2022, law enforcement started taking further action to shut down a number of illegal operations. However, unfortunately, this didn’t have a massive impact, as many new operations and websites were created within a day.
It’s not all doom and gloom, though. Stories such as this one from May 2023 highlight authorities in the US and Europe arrested over 300 people in seizing a dark web drug trafficking marketplace. The article mentions over $53 million were also confiscated in the process.
As the authorities continuously try to track and stop illegal dark web activities, internet giants such as Google are also trying to spread awareness and encourage protective measures for consumers. In May 2023, they announced a new tool for Gmail users which will allow account owners to see if their email is being used on the dark web.
So, what should people know before accessing the dark web?
Legal consequences: if you access the dark web with the intent to purchase or sell any of the items listed earlier in this article, you could face severe consequences. This includes potentially facing legal consequences, even if you only stumbled onto a website by mistake.
Malware or hacking: without proper security in place, by accessing the dark web you become highly vulnerable to potential cybercriminals accessing your device. Scammers are also known to scam other criminals by creating counterfeit, malware-riddled versions of popular downloads like WormGPT. There is a high risk for your device to become infected by malware or viruses.
Lack of surveillance: venturing into the dark web can mean venturing into the unknown, and because of the nature of the dark web and the risks assumed by accessing it, there’s very little action you can take if someone targets or scams you.
How to protect yourself and your data from being leaked on the dark web
Well, like anything, the first step to preparedness is awareness. A recent article by Statista states 70% of adults worldwide are said to be unfamiliar with the dark web – a glaring statistic when we consider the level of risk and activity going on beyond the surface web.
Always use 2-FA or MFA whenever possible, especially on highly sensitive accounts such as online banking. Having a multi-factor login set up makes it harder for hackers to access your highly sensitive accounts and information.
Do not reply to suspicious messages or click suspicious links – this is incredibly important. Be critical before clicking links or divulging personal information. Get comfortable understanding what phishing is and what all the different types of phishing attempts can look like.
Change passwords regularly – in the event that your login details have been exposed in a hack or data leak, continuously changing and updating your passwords makes it harder for someone to access your accounts.
Keep your devices up-to-date, which includes continuously updating and anti-virus software and firewall protections.
Invest in protective measures, which can look like anything from high-security anti-virus software to solutions designed to combat the work of cybercriminals. For example, Eftsure is used by thousands of businesses in Australia, New Zealand, and the US to identify and stop cyberattacks like business email compromise.
Summary:
The surface web is the portion of the World Wide Web that can be indexed by search engines, such as Google, Yahoo, or Bing whereas the deep web is the portion of the internet that cannot be indexed by search.
The dark web is intentionally hidden and anonymous and cannot be accessed by an everyday browser. Tor Browser is the main browser used to access the dark web and it requires awareness and caution before attempting to do so.
The dark web has both legal and illegal uses.
It’s important to be aware of the dark web and learn how to protect yourself and your data from being accessed for illicit activities.