Benefits
Platform
Vendor Management
Onboard, verify and manage suppliers
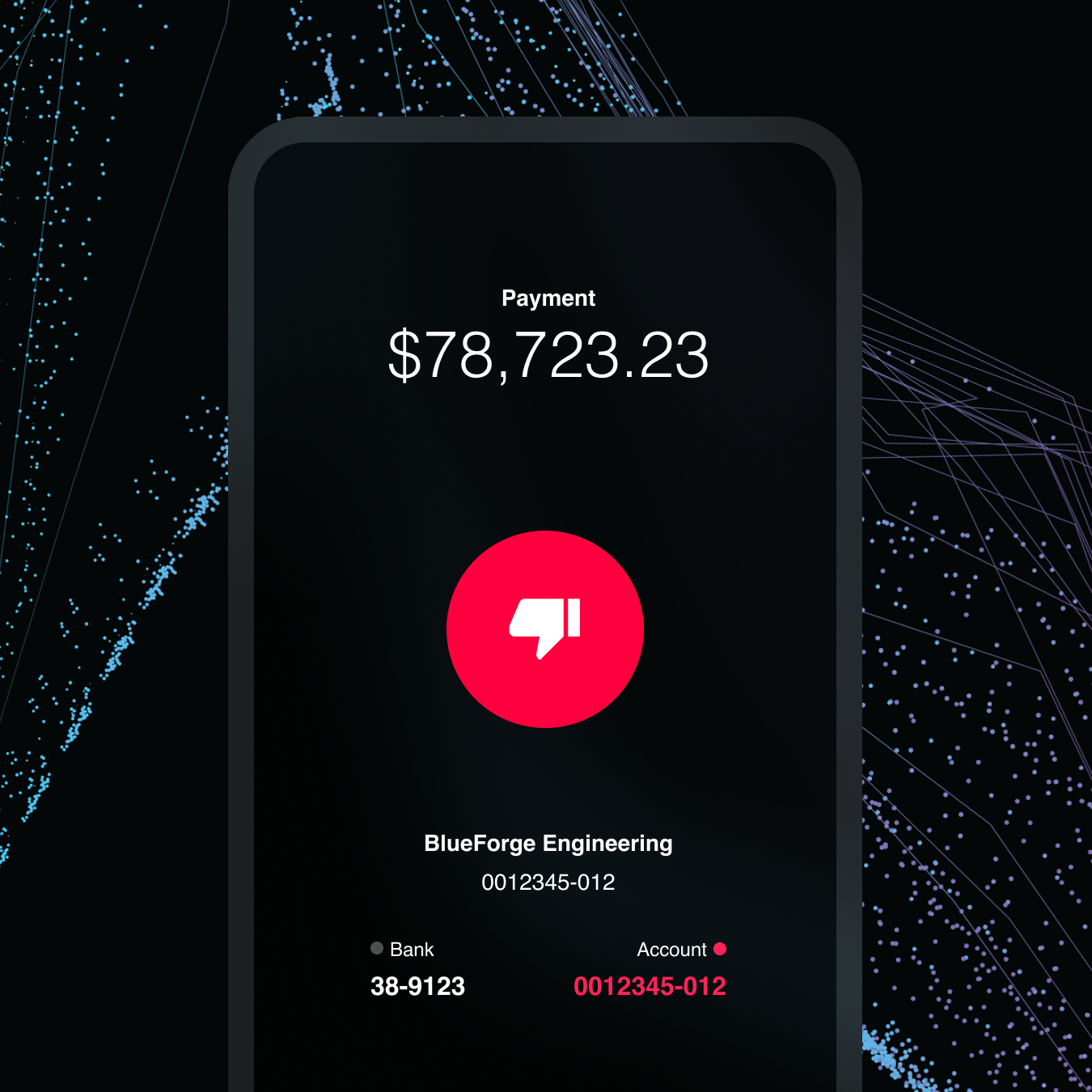
Payment Protection
Prepare, and pay with certainty
Segregation of Duties
A digital interface to manage visibility and assigned tasks
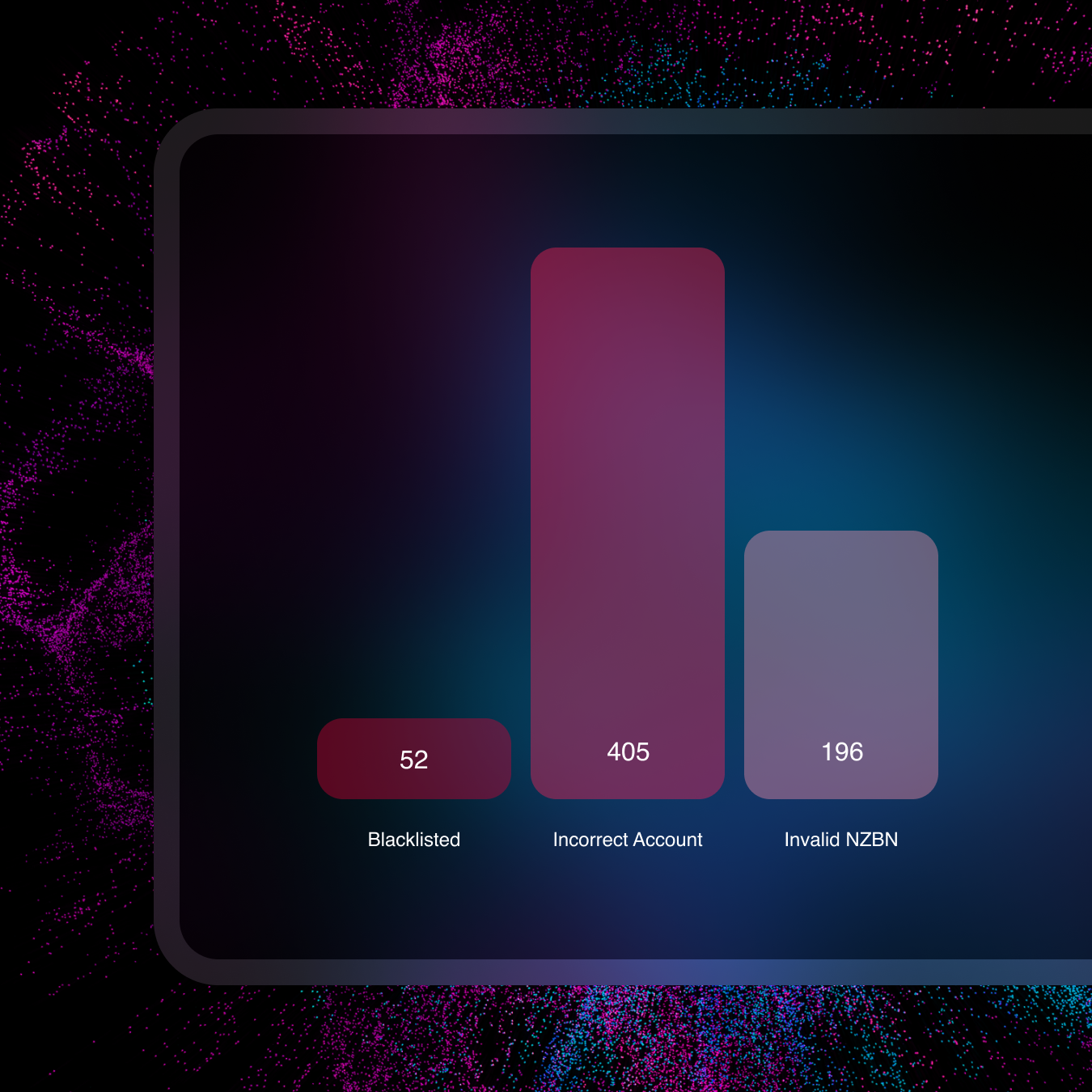
Audit and Report
Centralise reporting to reduce audit stress
Integrations
Robust integration capabilities with various platforms
By Role
By Threat
AI Deepfake fraud
Safeguard against AI deepfakes
Business Email Compromise
Advanced protection against Business Email Compromise
Insider Threat and Internal Fraud
Detect and deter internal fraud risks
CEO and executive impersonation fraud
Identify and block impersonation attempts
Invoice Fraud
Keep payments safe from fraud