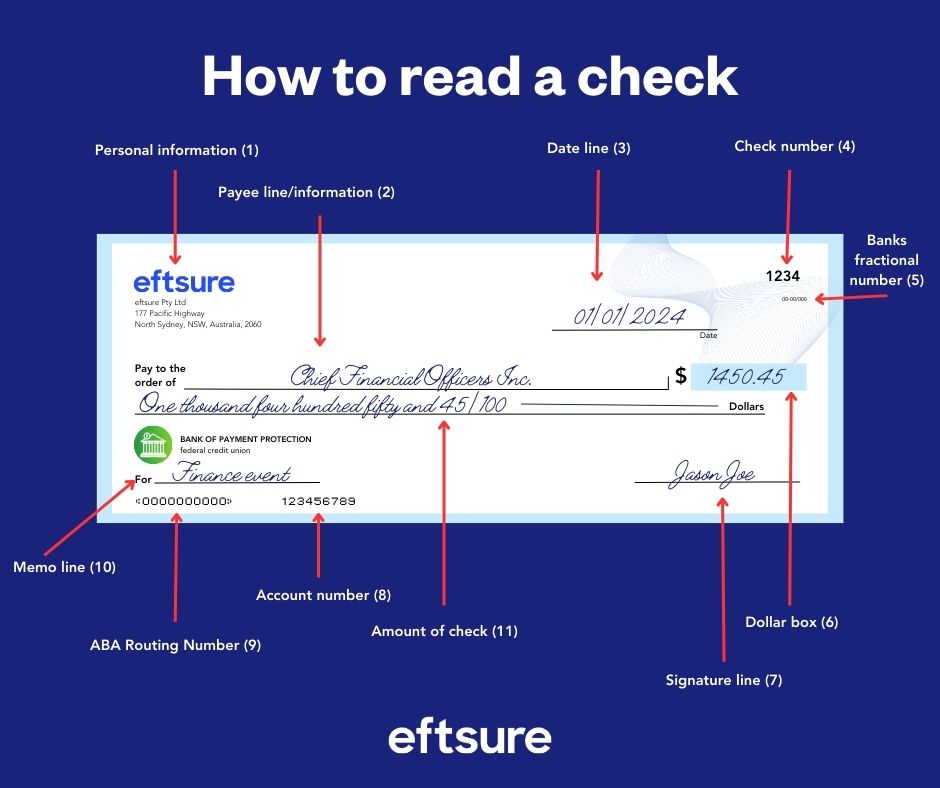
What Can Scammers Do with Your Phone Number?
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
Bank account number verification is an important part of fraud prevention. It also ensures the accuracy of financial transactions and, more broadly, protects the personal details of both individuals and businesses.
Here are some best practices on how to check (and verify) an account number.
An account number is a unique identifier assigned to a specific bank account or financial institution. While some account numbers feature up to 17 digits, the typical length is between 8 and 12 digits.
The account number works with other identifiers to ensure funds are sent to the intended recipient.
These include:
There are various ways to find a bank account number depending on the context and type of payment involved.
On a bank statement, the account number can be found at the top above the list of recent transactions.
Some statements will also have an “Account Details” section with important information (such as checking account number) in one place.
Account numbers also appear at the bottom of a paper check (usually between the routing number and the check number).
Accessing your bank account online or via a mobile app will also reveal the account number.
Look under “Account Details” or “Account Summary” or “Profile Settings” on the home screen or dashboard.
In some cases, it is possible to utilise specialised tools and services to verify account numbers.
Customers of some banks can verify account numbers over the phone. However, it should be noted that these services do not provide the account holder’s name.
Other banks offer verification services to ensure that the account number entered for a payment matches the one held by an individual or business.
Commonwealth Bank’s NameCheck is one example. It searches available payment data for a match and is relevant to customers making a first-time payment in Netbank.
If no match is found, the customer is prompted to take additional steps to verify the intended recipient.
Banks also use third-party account verification services such as Plaid and Yodlee. These services offer APIs that connect to a bank’s platform and verify account ownership before payments are processed.
Despite banks offering these services, there is still a high risk for consumers and businesses to become victims of fraud or potential human error. It’s always important to verify account numbers, especially when it comes to paying invoices for suppliers. Many companies will lean into a payment verification technology, like Eftsure, to bring the risk of payment error down to a minimum.
Before a payment is approved on the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network in the United States, a zero-dollar test transaction is sent to verify that the bank account number, routing number and other details are correct.
ACH file validation is another verification process that checks for the accuracy and completeness of data in a payment before it is submitted.
This step ensures that the information provided (such as the bank account number, routing number, transaction amount and payment details) complies with the necessary formatting and structural rules set by NACHA – the overseer of the ACH network.
For international transfers, several online tools can confirm whether the IBAN is valid. Since the IBAN is a relatively long string of letters and numbers, it is often entered incorrectly in the payment process.
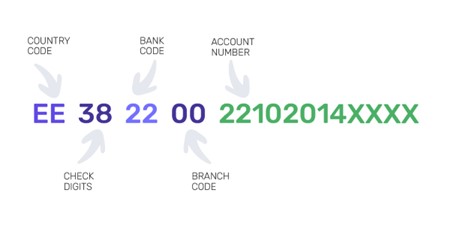
The validation process for an IBAN comprises six steps:
Summary:
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
When Mr. Beauchamp watched a video of Elon Musk – the world’s richest man – recommend a certain investment platform to make …
Your company delivered the good or service it promised to a client and now it’s time to collect the funds owed to …
Eftsure provides continuous control monitoring to protect your eft payments. Our multi-factor verification approach protects your organisation from financial loss due to cybercrime, fraud and error.