What is MFA?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to prove their identity using two or more distinct factors before accessing …
Passive authentication verifies a user’s identity without requiring them to take any explicit action.
Instead, passive systems monitor and analyse various data points in the identity verification process. These can include behavioural patterns, biometrics, device information, location data and even typing speed.
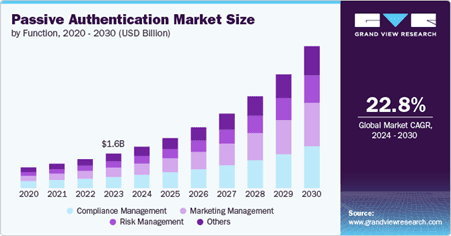
Driven by the need for seamless, secure and compliant user authentication, the market for passive authentication solutions is expanding rapidly. Indeed, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.8%, the market is expected to be worth USD 6.77 billion by 2030.
Traditional authentication methods such as passwords require the user to perform certain actions. This is also known as active authentication because the process follows a challenge-response format.
In a passive authentication process, however, the user is not required to perform specific actions. Verification instead relies on matching the current behaviour of a user with their historical behaviour.
To better understand this concept, consider some of the key data points used in passive authentication.
In device recognition, the system checks if the user is accessing the account from a recognised device. If the user always logs in from their laptop or smartphone, for example, this habit becomes part of the authentication process.
Behavioural biometrics involves analysis of how the user interacts with their device and may incorporate their typing speed, mouse movements or the way they swipe on a touchscreen.
These subtle behaviours create a unique behaviour profile that is near-impossible for an attacker to replicate.
Verification systems may also track the user’s location based on IP address or GPS data. If a user suddenly tries to access an account in an unusual location, the system may treat it as suspicious.
Monitoring network connections and patterns can also help identify suspicious activity. One potential red flag is the use of a VPN.
Collectively, the four elements described above create a holistic view of the user’s identity. If any patterns or behaviours deviate from the norm, the system may seek additional verification from the user or block access entirely.
Like many related processes, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are integral to passive authentication. Primarily, they enable systems to continuously verify user identity without direct input.
Here’s how.
Based on data collected from the data points described above, ML models learn what constitutes normal behaviour. They can also adjust for natural shifts in behaviour – for example, if a person’s typing speed improves over time.
ML models use sophisticated statistical techniques to identify subtle variations in user behaviour. These deviations may not be visible to traditional security measures but can be indicative of fraud or unauthorized access.
Passive systems make decisions in real-time and continuously analyse data to authenticate users as they interact with a system.
In an online banking app, for instance, AI can monitor the user’s actions for the duration of their session (and not just at login).
The scalability of AI models is not without its obstacles. However, these models remain the most effective way to analyse vast amounts of financial data.
For interconnected financial institutions with millions of customers, AI enables them to authenticate identities without manual intervention and spot anomalies that would otherwise evade human detection.
Models are also able to adapt and learn, which is a critical skill to counter the increasing diversity and sophistication of cyberattacks.
Numerous benefits of passive authentication make it attractive to both consumers and businesses.
One obvious benefit of passive authentication is that it does not detract from the user experience.
Traditional authentication methods add friction, particularly if they require multiple steps or the recall of complex passwords. For businesses, the impact of a poor user experience on revenue can be substantial.
Research indicates that 82% of online shoppers are more likely to purchase from a vendor if they already have an account. What’s more, almost 50% failed to complete a transaction because of a problem with authentication.
By essentially working in the background, passive authentication allows customers to access their accounts and make purchases with less hassle.
Unlike static forms of authentication that only verify identity once, passive authentication provides continuous monitoring across each user session.
Even if a fraudster manages to access an account with stolen credentials, passive authentication can detect unusual behaviour mid-session and take appropriate action.
In this way, passive systems address many of the vulnerabilities of password-based systems. Namely, their exposure to brute-force attacks, account takeovers, credential stuffing and numerous types of phishing attacks.
While traditional fraud detection systems can sometimes treat authentic users as suspicious, passive authentication is more accurate because it assesses multiple factors simultaneously.
This reduces the number of false positives and ensures that legitimate users are not burdened with unnecessary account lockouts or superfluous verification measures.
Passive authentication introduces the notion that authentication is both adaptive and risk-based. In other words, the level of scrutiny in the user verification process dynamically adjusts based on the level of perceived risk.
While active authentication methods have become more nuanced, they still employ a one-size-fits-all approach where each user is subject to the same level of scrutiny (irrespective of past behaviour).
Powered by AI and ML, passive systems continuously monitor user patterns to identify anomalous behaviour, but they also enable routine activities to proceed with minimal intervention.
Summary:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to prove their identity using two or more distinct factors before accessing …
Imposter scams are a type of fraud where scammers pretend to be trusted individuals, companies, or government agencies to deceive victims into …
Accounts payable fraud is a deceptive practice that exploits vulnerabilities in a company’s payment processes. It occurs when individuals—whether employees, vendors or …
Eftsure provides continuous control monitoring to protect your eft payments. Our multi-factor verification approach protects your organisation from financial loss due to cybercrime, fraud and error.