What is RAT malware?
Remote access trojan (RAT) malware is malicious software that permits cybercriminals full, unauthorised remote access to a victim’s computer. Once installed, the …
A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement, is a report that outlines your net profit for a certain period of time, such as one month or one year. This financial statement summarizes your revenue and operating expenses, giving detailed information about how your business is generating revenue, managing costs, and making profits.
P&L statements are one of the three main financial statements, alongside the balance sheet and cash flow statement. Businesses will usually generate these three reports together to give investors, lenders, and owners a snapshot of the financial performance of the company during the period.
If you’re a business owner, you’ve probably been asked to provide a profit and loss statement at some point. Many organizations use profit and loss statements to make informed decisions. Here are some of the people that might request this document:
Profit and loss statements can be generated in two different ways: cash and accrual. Cash basis financial reports only show transactions that cleared the bank account during the time period. On the contrary, the accrual method of accounting will generate a profit and loss statement with revenue and expenses incurred, but not received or paid.
Regardless of the accounting method used, P&L statements will all contain the same sections, including:
Within each of these categories, there will be subgroups of expenses. For example, your cost of goods sold category could contain machinery depreciation, wages, raw materials, and freight.
The bottom-line number on your profit and loss statement, also known as net income, is a crucial number that summarizes your profitability for the period. Calculating net income can be done with the following formula:
Revenue – Expenses = Net Income
However, there are other formulas that you can calculate from your profit and loss statement. Here is a more detailed breakdown of the net income formula:
Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses = Operating Income – Other Income/Expense = Net Income
Using this formula allows you to calculate other important metrics, like gross profit margin and operating income. These numbers play a vital role in evaluating the financial health of your business operations.
The P&L statement is a fundamental financial statement for a reason. It provides key information about business performance, informing leaders and stakeholders on a variety of different things.
Comparing profit and loss statements can be done in a few different ways. Let’s cover a few of the comparison strategies in more detail:
When it comes to comparing the P&L statement between periods, you need to have a standardized process. For example, using net profit margin in one period and sales growth in another won’t give you comparability. Create a list of analysis tasks and track them each period to maximize insights.
Profit and Loss Statement Example
Many companies are required to issue audited profit and loss statements. Below is Amazon’s 2023 profit and loss statement.
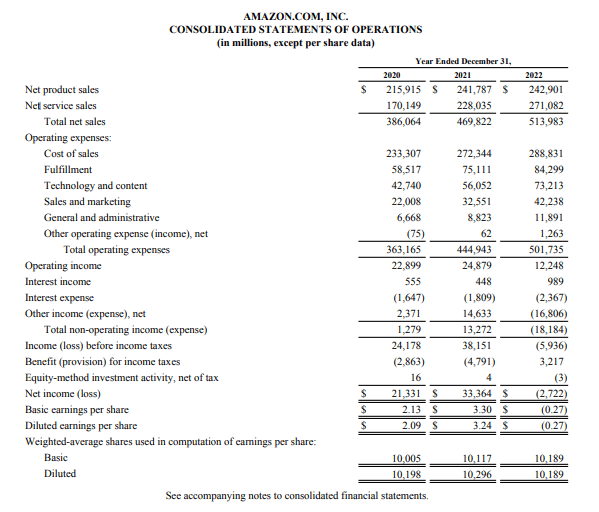
From looking at this statement, we can see that Amazon breaks out total sales by service and product. In addition, their main expense categories include cost of sales, fulfillment, technology and content, sales and marketing, general and administrative, and other operating expenses. Each company will create a profit and loss statement template unique to their business operations. However, profit and loss statements are still subject to accounting principles established by regulatory authorities, like the FASB and IASB.
Creating a profit and loss report is relatively straightforward. Here are the steps involved:
Summary
Remote access trojan (RAT) malware is malicious software that permits cybercriminals full, unauthorised remote access to a victim’s computer. Once installed, the …
A PayPal invoice scam is a type of phishing scam where fraudsters send fake invoices from the PayPal platform to trick recipients …
Agent Zero (A0) is an open-source AI tool that doesn’t have the same restrictions as current AI tools available to users. This …
Eftsure provides continuous control monitoring to protect your eft payments. Our multi-factor verification approach protects your organisation from financial loss due to cybercrime, fraud and error.