What is Agent Zero?
Agent Zero (A0) is an open-source AI tool that doesn’t have the same restrictions as current AI tools available to users. This …
Deep-Live-Cam is a sophisticated deepfake technology that creates real-time video impersonations of individuals by manipulating live camera feeds with artificial intelligence. Deep-Live-Cam is an open source tool that allows for real-time face swapping and video deepfakes.
The technology enables fraudsters to participate in video calls whilst appearing as trusted executives, vendors or financial partners. Deep-Live-Cam includes a webcam mode for live streaming and video conferencing.
Deep-Live-Cam has become an especially destructive tool for criminals targeting financial transactions and payment authorisations. Moreover, anyone can use the tool with a standard PC and free software.
According to the Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2024, these AI-powered impersonations have increased in both speed and sophistication. Based on this trend, Gartner believes almost a third of enterprises will soon move away from biometric verification as their sole authentication measure.
Deep-Live-Cam is a revolutionary AI-powered tool that enables real-time face swapping and one-click video deepfakes using just a single image. This cutting-edge technology has been made open-source, making it accessible to a wide range of users, from artists and content creators to tech enthusiasts. With Deep-Live-Cam, users can transform live webcam feeds or static videos with unparalleled ease and accuracy, harnessing the power of artificial intelligence to seamlessly replace faces. Whether you’re looking to create engaging content or explore the possibilities of AI, Deep-Live-Cam offers a powerful and user-friendly solution.
Deep-Live-Cam boasts an impressive array of features that make it an indispensable tool for anyone looking to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation. Some of the main features of Deep-Live-Cam include:
Deep-Live-Cam is built on a robust technical foundation that enables it to deliver high-quality output video quality and seamless face swapping. Some of the key technical aspects of Deep-Live-Cam include:
By incorporating these sections, the article will provide a comprehensive and detailed overview of Deep-Live-Cam, highlighting its capabilities, features, and technical foundation while maintaining a consistent tone and style.
Deep-Live-Cam represents a significant evolution beyond static deepfakes and in the process, provides criminals with unprecedented capabilities to commit financial fraud.
Where earlier technology created only pre-recorded videos, Deep-Live-Cam enables interactive impersonations that respond naturally during live conversations. This undermines video verification procedures that many organisations have implemented to counter traditional fraud methods. In addition to real-time video impersonations, Deep-Live-Cam can swap faces in real-time, making it a powerful tool for creating video deepfakes.
The technology is used to:
Deep-Live-Cam operates via sophisticated neural networks trained on thousands of hours of video to understand facial movements, expressions and speech patterns. Such is their precision and accuracy that in one test, humans were only able to identify the presence of a deepfake 24.5% of the time.
Deep-Live-Cam started as an open-source project on GitHub, and like many other projects on the platform, combines several existing software packages into one interface.
To start, it detects faces in both the source and target images which, in this context, is a video frame. Users can select a target image or video to replace the original face in real-time. Pre-trained AI models then swap the faces before GFPGAN—an AI-powered face restoration model—enhances facial detail and removes artifacts. The output file containing the swapped frames is saved in a specific directory once processing is complete.
When combined, each component:
For AP departments, Deep-Live-Cam presents a major shift in fraud risk. With one click video deepfake capabilities, fraudsters can easily create convincing deepfakes to deceive AP teams.
Few employees can spot a deepfake impersonation in real-time, and, in any case, may be compelled to contravene company policies because of social engineering tactics like forced urgency.
Here are some other vulnerabilities that Deep-Live-Cam is well-placed to exploit.
1. Video-based payment authorisations
Many companies have implemented video verification calls as an enhanced security measure for the approval of major transactions.
Deep-Live-Cam directly compromises this control because it allows fraudsters to impersonate key personnel and convince AP staff to proceed with unauthorised transactions.
2. Emergency payment scenarios
Fraudsters can fabricate video calls and then pose as company executives in crises that require immediate wire transfers.
The visual confirmation that Deep-Live-Cam affords makes these scenarios considerably more believable than phone or email-based approaches.
3. Vendor impersonation and contract modifications
Here, criminals impersonate established vendors and request payment changes or contract modifications. These interactions are often followed by fraudulent invoices that reflect key details of the discussion.
Deep-Live-Cam attacks continue to evolve as criminals develop more advanced approaches. Indeed, what started as a harmless AI tool for creators in the media industry has now transformed into a multi-layered weapon that can circumvent even the most robust protections. Deep-Live-Cam can create deepfakes using only a single image, making it highly efficient and accessible.
Primarily, the tool’s effectiveness relies on a combination of technical innovation and psychological manipulation.
Hybrid attack chains
Those seeking to create synchronised audio-visual deepfakes often pair Deep-Live-Cam with external tools capable of voice cloning or speech synthesis.
These complementary tools replicate the victim’s voice and enable the creation of more comprehensive deepfake content across multiple communication channels.
Meeting infiltration
Rather than initiate a call (which may be suspicious), fraudsters join scheduled calls and manipulate conversations while other attendees remain unaware.
This tactic exploits calendar information obtained from compromised emails, and by assuming the identities of certain participants, fraudsters can subtly influence payment-related decisions while benefiting from the inherent trust of an established meeting.
Verification system exploitation
Deep-Live-Cam can also defeat video-based payment verification systems by studying corporate protocols and tailoring impersonations to provide expected responses.
An AP team at a finance company may have a strict protocol for wire transfers over $50,000. The protocol requires a video call with the relevant executive who must provide three critical pieces of information:
A criminal wanting to target this company would first collect intelligence about the protocol via phishing and/or compromising the email account of someone in the finance department. Then, they could then use Deep-Live-Cam to impersonate the CFO with incredible deception.
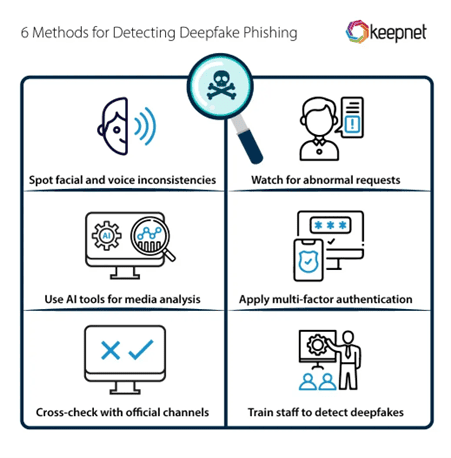
While tools like Deep-Live-Cam represent a formidable obstacle to traditional verification methods, companies can implement various countermeasures to protect themselves.
Central to this effort is the ability to move beyond single-factor verification to create layered security frameworks. In other words, frameworks that don’t rely exclusively on visual confirmation.
Finance departments must resist the temptation to act based on visual confirmation alone. They must also understand that in the age of AI-powered fraud, seeing is no longer believing.
A better strategy consists of:
· Multi-channel authentication. As noted above, it’s important to never rely exclusively on video verification. Implement parallel confirmation through separate, pre-established communication channels.
· AI detection. Tools use AI to analyse facial movements, eye blinks, and texture patterns to detect deepfake anomalies. They can also detect video frame inconsistencies and determine whether the video stream has been tampered with in an injection attack.
· Unpredictable verification questions. Develop authentication protocols that include questions whose answers wouldn’t be available in public records or social media.
· Artificial delay policies. Lastly, implement mandatory waiting periods for bank detail changes or transaction requests (irrespective of their apparent legitimacy).
In summary:
Agent Zero (A0) is an open-source AI tool that doesn’t have the same restrictions as current AI tools available to users. This …
First-party fraud occurs when an individual deliberately defrauds a business or financial institution by misrepresenting information or falsely disputing transactions for financial …
Invoice fraud is a deceptive scheme in which fraudsters manipulate invoices to trick businesses into making fraudulent payments. This form of financial …
Eftsure provides continuous control monitoring to protect your eft payments. Our multi-factor verification approach protects your organisation from financial loss due to cybercrime, fraud and error.