What is source-to-pay (S2P)?
Source-to-pay (S2P) is an end-to-end process in procurement that encompasses the activities associated with sourcing products from suppliers.
Synthetic identity fraud is a form of identity theft where criminals create new identities from a mixture of authentic and falsified personal information.
Unlike traditional forms of identity theft – where criminals steal the identity of a specific individual – synthetic identity theft involves the creation of an identity that does not correspond to a real person.
According to Thomson Reuters, this practice is the fastest-growing form of identity theft and is responsible for over 80% of all new account-related fraud.
Synthetic identity fraud is also costly, with Mastercard projecting that it will cost businesses almost $5 billion in 2024 alone.
Synthetic identification is used to commit fraud in four primary ways:
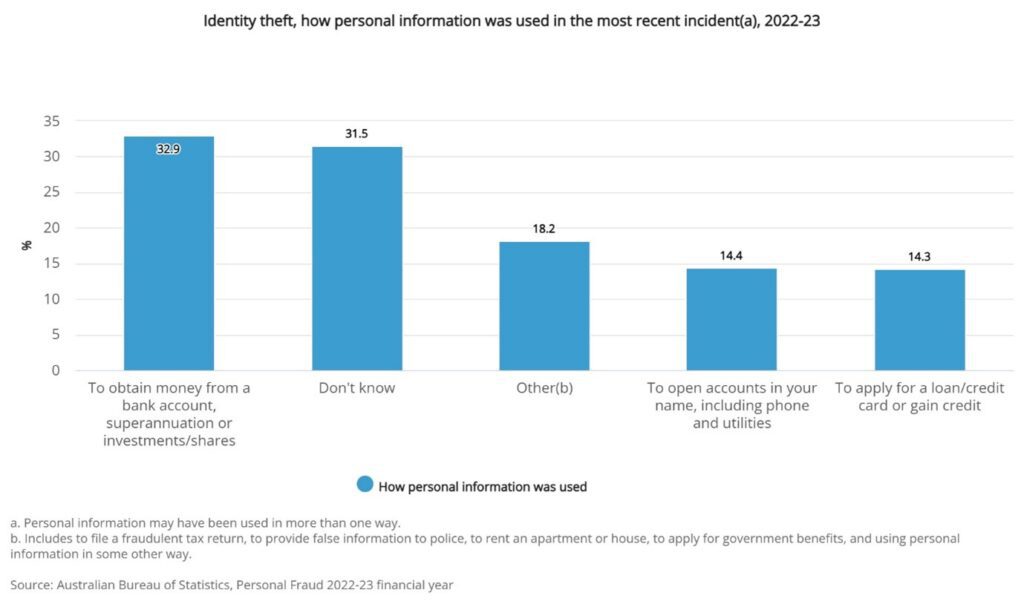
While methods depend on the end objective, this is how the synthetic identify fraud process works in the context of obtaining credit.
Malicious actors start by combining real and fake information about a person to create a synthetic identity.
In the United States where identity verification relies heavily on personally identifiable information (PII) – criminals use the victim’s social security number (SSN) as the basis of the new identity.
In Australia, the SSN is substituted with a tax file number (TFN), Medicare card, or passport.
Particularly vulnerable are children, the elderly, the homeless, and anyone else who does not possess a credit history.
Fraudsters then combine this stolen authentic information with other fake details like email address, postal address, name, or date of birth.
The final product is sometimes referred to as a “Frankenstein identity” because of the way disparate pieces of information are assembled.
With the synthetic identity created, criminals then build a credit profile by making applications for loans and credit cards.
While the first application is typically rejected, this process alone establishes a credit history with the major credit reporting bureaus. Fraudsters will continue to make applications until they are accepted (often by a high-risk lender).
Others will use the piggybacking strategy, where the fraudulent identity is added to the account of a third-party with good credit. In exchange, the third-party may receive financial compensation.
Criminals exercise extreme patience when building their credit history.
They will develop an attractive credit score over months or even years by making authentic purchases and ensuring that repayments are made on time.
This behaviour mimics the actions of a real person, and the trust it engenders is utilised to make subsequent credit applications.
This is sometimes referred to as the profit stage.
In a strategy known as pollination, some fraudsters will use the positive credit history of their synthetic identity to add additional authorised “users” to the accounts that identity holds.
This process can be repeated indefinitely, enabling the individual to build a network of fraudulent IDs that pass trust to new credit histories.
There are two more options to exploit credit.
Fraudsters with an end goal in mind will max out their credit cards or obtain new loans, default on their repayments and then disappear without a trace.
Others who are looking to double their returns may notify lenders that their debt is the result of someone stealing their identity. Once their credit balance has been cleared by the lender, they will start the process of debt accumulation once more.
The three Ps of synthetic ID fraud: piggybacking, profit, and pollination.
Detecting synthetic identity fraud is inherently complex and difficult.
The identities criminals create cannot be traced back to a real person, and many will maintain multiple synthetic identities at the same time.
Banks also have a hard time identifying fraudulent applications because their systems tend not to flag them as suspicious.
What’s more, instances of synthetic identity fraud are either unrecognised or poorly understood by some financiers. Many instances will be written off as a credit loss since:
Detection is made harder still when one considers that those who are vulnerable to synthetic ID theft are also the least aware.
Individuals without a credit history (such as children) are less likely to access that history, which makes the timely identification of fraud unrealistic.
Synthetic identity fraud mitigation requires a comprehensive, holistic and modern approach.
Let’s take a look at how this can be achieved.
Synthetic ID detection is difficult, but for banks and customers, prevention is the best form of cure.
Individuals should protect their personally identifiable data at all costs and use software that protects their passwords and digital security.
As with many types of fraud, awareness is also key.
Individuals should be wary of unexpected communication from official sources and be able to recognise the hallmarks of a scam. They should also monitor their credit scores periodically to check for fraudulent activity.
Businesses, on the other hand, can use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to improve the detection process in two key ways:
Collaboration between public and private entities is also an important component of the identify fraud mitigation toolkit.
Governments hold verifiable information about their citizens, but if financial institutions cannot access it, they are ultimately forced to guess details the government already knows.
In the United States, action has been to taken to address this issue. The Social Security Administration now offers a service called electronic Consent Based Social Security Number Verification (eCBSV).
Permitted entities can use the service to verify whether a borrower’s SSN, name, and date of birth match governmental social security records. eCBSV also alerts entities if the individual attached to an SSN is deceased.
According to the Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (AUSTRAC), the minimum KYC requirements for an individual customer are their full name and date of birth or residential address.
However, to properly mitigate against synthetic ID fraud, businesses should enhance their KYC procedures with more data points and look for patterns.
For example, while data points such as an applicant’s date of birth or home address can be verified in isolation, there may be inconsistencies with how the data is provided.
Does an applicant’s name, address, and other sensitive information always appear together? Or does variation exist across different accounts or applications?
Businesses can utilise the services of data analytics providers to identify abnormalities and flag suspect applications. This process is near instantaneous such that the application process for legitimate individuals is relatively frictionless.
Growth in the prevalence of synthetic fraud has been driven by the ability of malicious actors to scale and repeat their efforts.
These individuals will often hit the same lender with multiple applications – particularly if they enjoyed early success. However, their efforts can be thwarted when they have to prove to the lender that each application is authentic.
Machine fingerprinting – also known as device fingerprinting – is a way for banks to detect multiple applications that originate from the same device.
Vast amounts of data can be collected on a device every time a web request is sent to a server, such as:
Ultimately, machine fingerprinting can provide clarity on whether the applicants are using a proxy or VPN to make applications appear as if they’re from different people.
The technique can also be used to identify suspect hardware configurations – another potential marker of synthetic ID fraud.
References
Source-to-pay (S2P) is an end-to-end process in procurement that encompasses the activities associated with sourcing products from suppliers.
Reading a check may appear straightforward at first glance, but the various elements that comprise a check play a crucial role in …
A hedging strategy is a risk management strategy to avoid large financial statement losses due to investment fluctuations. Hedges work like an …
Eftsure provides continuous control monitoring to protect your eft payments. Our multi-factor verification approach protects your organisation from financial loss due to cybercrime, fraud and error.