What Can Scammers Do with Your Phone Number?
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
ASIC form 388 one of the documents used to report information to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC).
There are multiple types of ASIC forms. One type relates to the registration of a new company, for example, while another is used to notify ASIC of changes to company details such as its name or office address.
The focus of this article will be Form 388 – a key part of the annual financial reporting requirements of some Australian and foreign-owned entities.
Form 388 is a cover sheet that accompanies the financial statement and associated reports of the disclosing entity.
All documents and the obligations that underpin them adhere to the relevant sections of the Corporations Act 2001.
Some of the components of the form include:
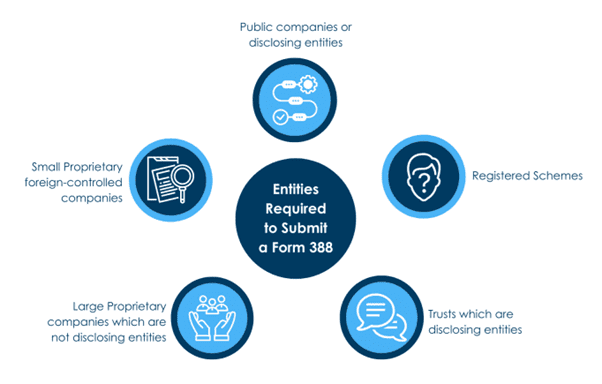
The entities required to submit Form 388 are:
Large proprietary companies are also required to submit Form 388 if they (and the entities they control) satisfy at least two of the following three criteria:
Companies that do not satisfy two of the above criteria are considered “small” and are exempt from lodging financial statements and reports.
However, in some circumstances, ASIC may still request they lodge if it has concerns over the company’s financial performance or compliance.
Other circumstances where a small propriety company may be required to submit Form 388 include:
The purpose of Form 388 is to ensure that entities comply with their obligation to lodge financial statements and reports with ASIC. It is also the mechanism by which these important documents are submitted.
In the process, the entity provides ASIC with a formal record of its financial performance and position.
This information promotes transparency and accountability with investors and creditors and also helps ASIC enforce financial standards if they are not met.
Deadlines for Form 388 submission depend on the type of entity.
Within 4 months of the end of the financial year:
Within 3 months of the end of the financial year:
Contact the auditor for an applicable timeframe:
Note that if the form is submitted late, a fee of $96 applies for all submissions less than a month after the due date. Forms submitted more than one month late will attract a late fee of $401.
Submission of Form 388 is free provided that the necessary documents are lodged by the due date. The only exception is the submission of a 388K Trust (disclosing entity) form, which attracts a lodgment fee of $1,485.
To view all applicable fees, learn more about the requirements for different entities or obtain a copy of the form, click here.
Summary:
References
https://asic.gov.au/regulatory-resources/financial-reporting-and-audit/preparers-of-financial-reports/are-you-a-large-or-small-proprietary-company/
https://asic.gov.au/regulatory-resources/forms/forms-folder/388-copy-of-financial-statements-and-reports/
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
When Mr. Beauchamp watched a video of Elon Musk – the world’s richest man – recommend a certain investment platform to make …
Your company delivered the good or service it promised to a client and now it’s time to collect the funds owed to …
End-to-end B2B payment protection software to mitigate the risk of payment error, fraud and cyber-crime.