What is vendor management?
Vendor management is the act of ensuring that your third-party vendors meet regulatory requirements and contractual obligations. This safeguards your business from …
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security measure that requires users to verify their identity with two separate authentication factors before accessing an online account.
Unlike the traditional approach of relying exclusively on a password, 2FA introduces an additional layer of protection.
Authentication factors, including the crucial authentication code, typically fall into one of three categories:
By combining two of these factors, 2FA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access. Even if a hacker steals a password, they still need the second factor to breach the account.
2FA’s importance to cybersecurity became evident in 2021 when Google made it mandatory for 150 million users. The move saw the number of compromised accounts drop by 50%.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires two different authentication factors to verify a user’s identity. This method adds an extra layer of protection to the traditional username and password combination, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information. By requiring two forms of verification, 2FA ensures that only the user can access a system, network, or application, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and protecting against various types of cyber attacks. In essence, two-factor authentication 2FA is crucial in safeguarding personal and organizational data from malicious actors.
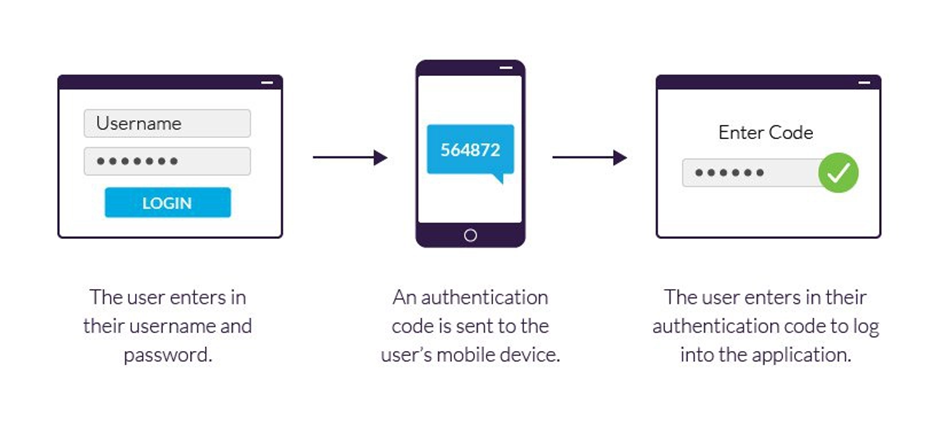
Two-factor authentication is straightforward and typically follows these steps:
This extra step may seem inconvenient, but it’s a small price to pay for significantly enhanced security.
Authentication factors are the methods used to verify a user’s identity, and they fall into three main categories: something you know, something you have, and something you are.
Two-factor authentication requires the use of at least two of these factors to verify a user’s identity, thereby enhancing the security of the authentication process.
There are several authentication methods that online platforms use to enable 2FA, and each method offers a different level of convenience and security.
Here’s a closer look at the most prevalent.
Apps like Google Authenticator and Authy generate time-sensitive, one-time passcodes on a mobile device that expire every 30 seconds.
To set up an authenticator app, a QR code linked to the online account is scanned before the app starts to generate login codes. Since these apps also work offline, they are extremely secure.
This method sends a one-time password (OTP) to a user’s phone via SMS. The user enters this code during login to verify their identity.
Security keys are physical USB or NFC devices that plug into a computer or connect via Bluetooth. These devices—such as YubiKey or Google’s Titan Key— authenticate users when inserted into the device.
This method uses unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns to verify identity. Many smartphones and some laptops support this method.
Specific devices can be designated as “trusted” so that 2FA prompts are bypassed. This method is often used in combination with other 2FA methods.
Cybersecurity experts agree that 2FA is one of the most effective ways to protect online accounts.
It delivers various benefits:
Implementing two-factor authentication involves several key steps, starting with choosing an appropriate authentication method. Organizations can select from various 2FA solutions, including SMS-based 2FA, token-based 2FA, and biometric-based 2FA. The chosen solution should meet the organization’s security needs and be user-friendly. Once a solution is selected, it must be configured to work with the existing systems and infrastructure. This may involve integrating the 2FA solution with authentication systems like Active Directory or LDAP. Proper implementation ensures that the authentication process is seamless and that users are granted access securely.
While 2FA requires two forms of user authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires two or more factors and provides an additional layer of security.
Another way to think of the relationship between 2FA and MFA is that the former is a type of the latter. In other words, all 2FA processes are a form of multi-factor authentication, but not all MFA involves just two factors.
To conclude, let’s explore some common 2FA mistakes and what employees can do to avoid them:
1. Over-reliance on SMS – use authenticator apps or security keys instead of SMS because of its vulnerability to SIM-swapping.
2. Failure to back up access codes or recover keys – if a device that contains these codes is lost or damaged, users may be locked out of accounts. Always save backup recovery codes in a secure location.
3. Over-reliance on trusted devices – avoid using the same trusted device for multiple accounts. If the device is compromised, scammers have more scope to steal data and commit fraud.
4. Over-reliance on a single 2FA method – if a 2FA method that relies on internet access fails, access to accounts may be lost. Incorporating security keys and authenticator apps is therefore crucial.
Key takeaways
Vendor management is the act of ensuring that your third-party vendors meet regulatory requirements and contractual obligations. This safeguards your business from …
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to prove their identity using two or more distinct factors before accessing …
Imposter scams are a type of fraud where scammers pretend to be trusted individuals, companies, or government agencies to deceive victims into …
End-to-end B2B payment protection software to mitigate the risk of payment error, fraud and cyber-crime.