What Can Scammers Do with Your Phone Number?
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
A finance report tracks and analyses financial information in a business. Financial reports are relied on by members of management, business owners, investors, lenders, and other third parties.
Businesses in the United States will generally issue financial reports in compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards look to streamline reporting for all businesses, giving investors and lenders more comparability. Businesses that operate globally will often comply with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Annual financial reports are the most common timeframe used; however, some public companies are required to issue quarterly financial statements for investors. Nevertheless, most small business owners will issue annual reports and use the data to file tax returns.
Financial reports can track different things, including profitability, overall financial health, and liquidity. There are three main financial reports, including:
This finance report tracks the revenue and expenses of your company for a specific period of time. By breaking down different income streams and expense categories, you are able to see the financial performance of your company, including overall profitability.
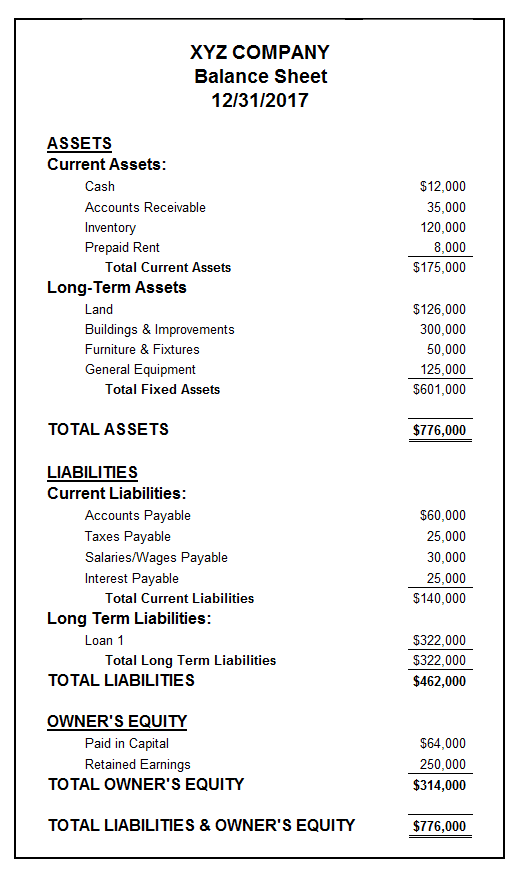
This financial report tracks the overall financial health of your business, including outlining what you own, owe, and have earned since the inception of your company. Your balance sheet has three main components: assets (items you own), liabilities (items you owe), and retained earnings (what you’ve earned, withdrawn, and contributed).
This finance report tracks movements in your cash accounts. There are three main sections on a statement of cash flows, including cash flows from operations, cash flows from investing activities, and cash flows from financing activities.
Financial reports are useful for a variety of reasons, from clarity into your business’s financial condition to documentation when looking to secure a new loan or investor. Here are a few more goals of financial reporting:
Investors need to know how their capital is being deployed in your organization. Ineffective use of capital can lead to low returns. With comprehensive annual reports, investors can evaluate the financial data of your business and determine if they want to continue investing or reallocate their funds elsewhere.
Cash flow management looks to improve the cash flowing in and out of your business. A positive cash flow indicates your business earns more than it spends, while a negative cash flow highlights that your business is losing money. Effective cash flow management helps your business scale and remain profitable, which is one of the goals of financial reports.
Monitoring your assets, liabilities, and equity is important as a business owner. For example, if you take on too much debt, your business might not be able to repay them. Financial statements track the financial position of your business, helping you remain agile in your decision-making.
When engaging in finance reporting, it’s important to ensure that the data in your accounting system is accurate. Here are a few tips to ensure accuracy in your finance reporting:
Summary
Verifying the accuracy of your financial statements can be done by looking over transaction classifications, completing monthly bank reconciliations, using specialized reporting software, and working with an acc
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
When Mr. Beauchamp watched a video of Elon Musk – the world’s richest man – recommend a certain investment platform to make …
Your company delivered the good or service it promised to a client and now it’s time to collect the funds owed to …
End-to-end B2B payment protection software to mitigate the risk of payment error, fraud and cyber-crime.