What is source-to-pay (S2P)?
Source-to-pay (S2P) is an end-to-end process in procurement that encompasses the activities associated with sourcing products from suppliers.
A cyber security incident response plan (CSIRP) is a documented strategy that clarifies how an organisation will respond to malicious actors and cyber threats.
The overarching objectives of a CSIRP are to:
Cyber-attacks are increasing in prevalence and severity, with the average small business losing $39,000 to malicious actors.
What’s more, a 2024 MYOB survey found that 60% of mid-sized Australian businesses had experienced a cyber-attack or related incident.
These attacks are also becoming more sophisticated. Keeper Security’s survey of more than 800 IT leaders reported that:
The above data shows that cyber security incident response plans have never been more crucial. The most obvious benefit is that they provide structured protocols to swiftly respond to threats.
On a broader level, CSIRPs ensure business continuity, protect sensitive data and increase organisational resilience.
The particulars of a CSIRP will vary from one business to the next, but the most effective plans take inspiration from five phases defined by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC).
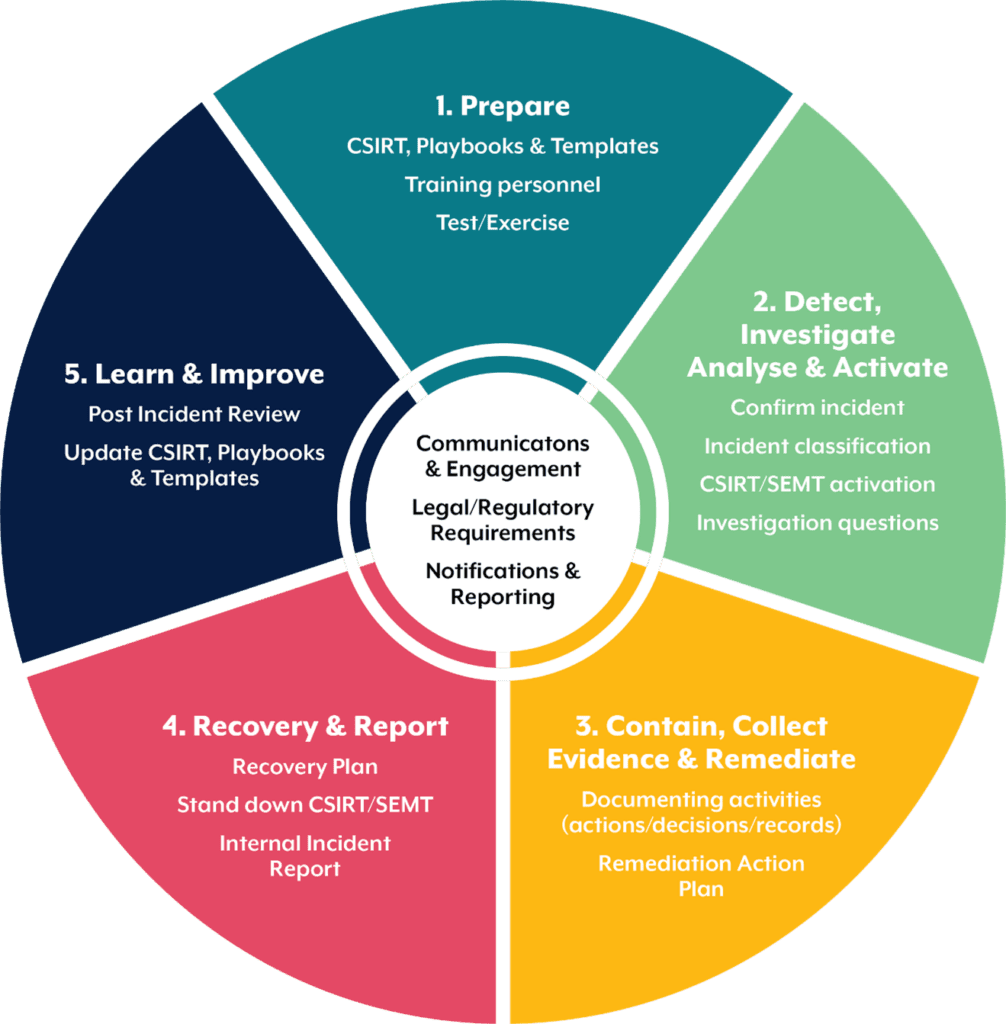
The most prepared organisations are those that have a CSIRP in place before a security breach occurs.
Preparation is a broad and multi-faceted topic. Nevertheless, robust incident response plans should detail:
The second phase comes into play when an incident has occurred and the organisation needs to respond.
Threats take many forms and are constantly evolving, so it is impossible to devise a plan for all of them.
However, a good starting point for any CSIRP is to consider the most common methods of attack:
If a potential threat has been identified, the CSIRP must account for how it would be investigated. Investigation involves comparing unusual activity or behaviour to baseline data and if necessary, preserving that data as forensic evidence.
The investigation sub-component also determines how a business would respond if alerted to an anomaly by a third-party security provider or the ACSC.
Analysis involves a systematic examination of the threat to understand its nature, scope and impact.
Analysis should also clarify how incidents are categorised, classified and prioritised as well as how data is stored and transmitted.
In sensitive cases, out-of-band transmission (such as communication that occurs over Slack) may be necessary.
In this context, activation is the mobilising of a cyber incident response team (CIRT) to manage the threat or incident.
As we touched on earlier, roles and responsibilities should be pre-assigned.
Most incidents require containment before they overwhelm a company’s resources or inflict further damage.
Containment is a critical part of the incident response process since it gives teams time to develop a tailored remediation plan.
Central to the remediation plan is decision-making. Should the system be shut down or disconnected from the network? Do certain functions need to be disabled?
In any case, the best course of action depends on:
Evidence collection is important should the matter progress to legal proceedings. But the business must collect evidence lawfully lest it be inadmissible.
Examples of evidence include IP addresses, databases, screenshots, CCTV, network packet captures, social media posts and configuration files.
Evidence should be stored in a secure location and be ready to present to third-party stakeholders.
Data should also be kept in an evidence log that details:
With the threat contained and evidence collected, a remediation action plan must be devised.
This plan outlines what actions and resources are required to resolve the incident, who is responsible, what systems should be prioritised and how long remediation is expected to take.
In the fourth phase, the organisation must craft a recovery plan to explain how compromised networks, systems and applications will be restored to normal operations.
Recovery also calls upon the organisation to detail:
In the fifth and final phase, a Post Incident Review (PIR) should be conducted.
The review should include a root cause analysis and a debrief on the incident response itself.
To that end, the seven-part PPOSTTE Model is sometimes used to reflect on what went well, what could be improved and whether the incident could have been prevented.
The NIST incident response framework (formally the NIST Cyber Security Framework 2.0) was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the United States.
NIST – who developed the framework as part of its duties under the Federal Information Security Management Act – details standards and best practices around information security for federal agencies.
NIST has also released a number of security incident handling guides tailored to non-government organisations.
Some are listed below.
Quick-Start Guide for Creating and Using Organizational Profiles
This publication helps develop organisational profiles to understand, tailor, assess and prioritise cybersecurity outcomes.
Profiles are based on factors such as the threat landscape, the business’s mission statement and stakeholder expectations.
A Guide to Creating Community Profiles
This NIST framework assists organisations with developing community profiles for cyber security risk management.
Note that the term “community” denotes a group of organisations with shared interests, objectives and contexts. They may be grouped by sector (e.g. critical infrastructure), technology (e.g. the cloud) or other use cases.
Small Business Quick-Start Guide
This release targets small and medium-sized businesses with modest or non-existent cyber security plans. Included under this umbrella are non-profits, small government agencies and schools.
The small business publication is not a standalone product but instead supplements the NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF) mentioned earlier.
References
Source-to-pay (S2P) is an end-to-end process in procurement that encompasses the activities associated with sourcing products from suppliers.
Reading a check may appear straightforward at first glance, but the various elements that comprise a check play a crucial role in …
In finance, internal controls are processes that ensure and maintain the integrity of financial and accounting information. These controls foster accountability, safeguard …
End-to-end B2B payment protection software to mitigate the risk of payment error, fraud and cyber-crime.