What Can Scammers Do with Your Phone Number?
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
An ABA number is a nine-digit number used to identify specific financial institutions in the United States.
ABA numbers (also called bank routing numbers or routing transit numbers) were introduced in 1910 by the American Bankers Association to ensure paper checks were delivered to the correct bank.
Today, there are more than 28,000 ABA numbers in active use.
In today’s digital age, ABA numbers are used in numerous contexts.
These include:
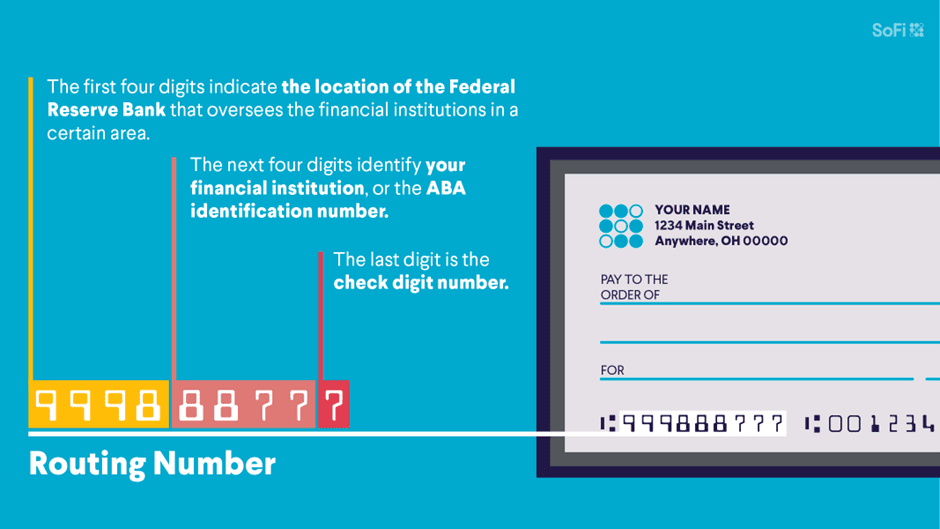
ABA numbers can be better understood by explaining their three constituent parts. Note that each part serves a specific purpose to ensure that funds land in the correct bank account.
The Federal Reserve Routing Symbol comprises the first four digits of the ABA number.
The first two digits clarify the Federal Reserve District in which a Federal Reserve Bank branch is located. Note that each branch oversees check and electronic payments on behalf of banks and other financial institutions.
For example, the ABA number for a branch in the First Federal Reserve District (Boston) starts with 01, while a branch in the Twelfth Federal Reserve District (San Francisco) starts with 12.
There are twelve districts in total, with each district spanning multiple states.
Other two-digit identifiers denote more specific use cases.
Examples include:
The third digit of the Federal Reserve Routing Symbol represents the check processing center assigned to the bank. However, thanks to the proliferation of electronic payments, only one such center remains in Atlanta, Georgia.
The fourth digit clarifies the bank’s location, with numbers assigned based on which state the bank occupies within its Federal Reserve District.
The ABA Institution Identifier identifies the financial institution within its Federal Reserve District. In other words, the financial institution the customer uses to send or receive money.
Issued by the American Bankers Association, the four-digit identifier helps distinguish between different branches of the same bank or credit union.
Financial services such as retail banking or mortgages may also be assigned unique identifiers in larger banks.
The checksum (or check digit) is the ninth and final digit in an ABA routing number. Calculated with a specific and complex algorithm, it ensures that the ABA number itself is valid and correctly formatted.
In practice, the checksum helps detect several types of errors. These include digit transpositions – where two digits in the ABA number are swapped – and single-digit errors where one of the numeric characters is incorrect.
ABA and ACH routing numbers are similar in that each contains nine digits and clarifies where funds should be sent.
But there do exist a couple of differences.
ACH routing numbers direct funds from one bank account to another and are associated with electronic payments on the ACH network. These numbers were introduced in the 1970s after an enormous volume of paper checks threatened to cripple the banking system.
ABA numbers, on the other hand, route funds between financial institutions on the ABA network and process both paper and electronic payments. In general, this makes them more widely accepted.
Summary:
When cell phones first became popular, no one thought they’d become what they are today. For the first few years, it was …
When Mr. Beauchamp watched a video of Elon Musk – the world’s richest man – recommend a certain investment platform to make …
Your company delivered the good or service it promised to a client and now it’s time to collect the funds owed to …
End-to-end B2B payment protection software to mitigate the risk of payment error, fraud and cyber-crime.